India has launched Project PRAGYASHAKTI, an ambitious initiative aimed at building a common integration framework for all its defense systems. The project seeks to enable seamless communication and data sharing among platforms of diverse origins from the United States, Russia, France, and the United Kingdom to those developed indigenously. This effort holds particular importance for the Indian Air Force, which operates one of the world’s most diverse fleets, making interoperability a critical need for operational efficiency and real-time decision-making.
Perfection is achieved, not when there is nothing more to add, but when there is nothing left to take away.
Antoine de Saint-Exupéry “Terre des Hommes (1939)”
Project PRAGYASHAKTI aims to develop a Common Electronic Warfare (EW) Software Framework. It focuses on achieving interoperability among various EW systems. The project seeks to enhance coordination between systems of different origins through a unified software architecture.

By implementing this project, developers aim to integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into EW analysis. The system will predict outcomes, analyze datasets, and standardize reports. Consequently, EW systems will exchange information efficiently and act in synchronization.
Core Objective of PRAGYASHAKTI
The main goal of PRAGYASHAKTI is to create an indigenous Integrated Electronic Warfare Software (IEWS) Framework. This framework will include eight specialized software packages, called Computer Software Configuration Items (CSCIs). Each package will handle distinct operational and analytical functions.
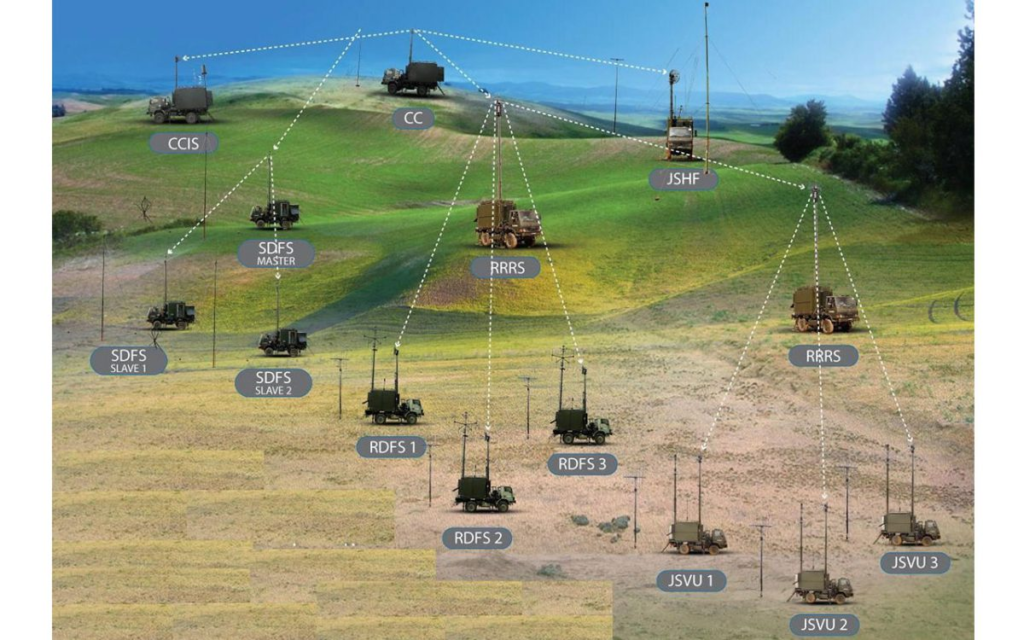
The framework will categorize its entities into four groups:
- Control Entities: System Level Control Centre (SLCC) and Block Level Control Centre (BLCC).
- Communication Entities: Reconnaissance & Direction Finding System (RDFS) and Jammer Station (JS).
- Radar Entities: Radar Entity (RSEC).
- Specialist Entities: Cellular, UAV, and Satellite Interceptors.
This classification ensures effective data management and seamless operational coordination between components.
Scope and Software Framework Development of PRAGYASHAKTI
The PRAGYASHAKTI project involves two major tasks development and implementation of the IEWS Software Framework.
Development Phase:
Eight unique software entities will be created to support radar, jammer, and interceptor operations. These software packages will form the building blocks of the integrated framework.
Implementation Phase:
The system will establish common operational standards across all entities. It will define generic entity types, standardize user interfaces, and unify message formats. This will ensure compatibility and efficiency throughout the network.
The implementation will also introduce:
- AI-assisted report analysis
- Integration with ICIC for analysis feedback
- Common databases for all sensor types
- Advanced message communication through OASIS MQTT 5.0
- Optimized data handling and dynamic report generation
Technological Enhancements and Common Features
The framework will feature an upgraded technology stack to improve performance and scalability. It will include simulators for testing and training. The addition of AI and ML will help perform predictive operational analysis.
The software will optimize system resources and database operations. It will maintain strict quality standards while supporting faster data transmission and secure communication.
Furthermore, the inclusion of a Generic Device Interface Layer will simplify connections with various EW devices. This modular approach will make upgrades and maintenance easier in the long term.
Development Methodology and Phases
The development process will follow an incremental model with two builds. Each build will progressively add new capabilities and improvements.
Phase 1 – Software Requirement Specification (SRS):
Teams will gather detailed requirements and create a comprehensive SRS document.
Phase 2 – Design Enhancements:
Developers will design system architecture, class structures, and database layouts.
Phase 3 – Implementation:
Coding and software realization will take place according to the defined scope.
Phase 4 – Integration Testing:
All system entities SLCC, BLCC, and sensors will undergo integration testing in a LAN environment. This will ensure compatibility and full compliance with operational standards.
Development Timeline
- SRS Document: T0 + 3 months
- Build 1 Realization and Testing: T0 + 15 months
- Build 2 Completion and Final Testing: T0 + 25 months
(T0 denotes contract placement date.)
Project PRAGYASHAKTI marks a vital advancement in India’s defense software ecosystem. It embodies self-reliance, innovation, and technological strength. The integration of AI, ML, and standard frameworks will strengthen India’s electronic warfare capabilities.
By ensuring interoperability, real-time data exchange, and predictive analysis, the project will empower defense operations with agility and precision. Ultimately, it will establish a robust foundation for future indigenous EW systems and reinforce India’s digital defense architecture.
Ah, Project PRAGYASHAKTI! Finally, an EW framework thats as organized as my sock drawer (but way more powerful, I assume). The meticulous classification of entities and the emphasis on standardizing reports sound almost… peaceful. Imagine SLCC, BLCC, and the RDFS having a calm meeting over coffee, while the JS and Jammer Station just trade witty banter. Kudos to the team for aiming for AI-assisted analysis and predictive operational insights – now if only my microwave could predict when the pizza is ready. This project is Indias digital shield, and honestly, it looks about as fun to build as solving a Rubiks Cube blindfolded, but way more important. Go, PRAGYASHAKTI, go!